
contributed by Ryan Schaaf & Jack Quinn
Every person enjoys video games.
Albert Einstein himself indicated they are one of the most elevated kind of investigation. He recognized video games are opportunities for something deeper and a lot more purposeful than a childish waste of time. Gamings advertise situated knowing, or in other words, discovering that takes place in teams of technique during immersive experiences. Frequently, playing games are the very first method youngsters utilize to explore higher-order reasoning skills related to producing, examining, analyzing, and using new expertise.
See additionally 50 Concerns To Assist Pupils Consider What They Assume
This write-up is composed in 2 parts. The initial, composed by Ryan Schaaf, Assistant Teacher of Technology at Notre Dame of Maryland College, presents gamification in an educational context, its numerous aspects, and some items that imitate gamified methods. The second part, shared by class instructor and train Jack Quinn, offers a firsthand account with perspective from a gamified understanding specialist. Below are our consolidated understandings.
Gamification In An Educational Context
Games have many aspects that make them effective cars for human discovering. They are typically structured for players to fix a problem; a crucial skill required for today and tomorrow. Several games advertise communication, participation, and even competitors among gamers. Several of one of the most immersive games have a rich story that generates creative thinking and creativity in its gamers. Ultimately, relying on exactly how they are made, video games can both teach and test their gamers. They are amazing bundles of training, finding out, and assessment.
The architectural aspects of video games are likewise particularly matched to offer this present generation of learners. Commonly called gamification (or gameful design according to Jane McGonigal), this strategy of adding video game aspects such as narration, analytic, aesthetic appeals, regulations, cooperation, competitors, benefit systems, feedback, and learning with experimentation right into non-game circumstances has already seasoned prevalent application in such areas as advertising, training, and consumerism with rampant success (see http://www.cio.com/article/ 2900319/ gamification/ 3 -enterprise-gamification-success-stories. html) for even more information.
In the education realm, gamification is starting to grab vapor. With success stories such as Classcraft, Class Dojo, and Rezzly leading the cost, the potential for gamification to infect increasingly more class is a forgone final thought. There are also pockets of educators in the teaching landscape that are creating their very own ‘gamefully-designed’ learning atmospheres. The following area explores such an atmosphere by sharing Jack’s experiences with his very own class.
See likewise 10 Details Ideas To Gamify Your Class
Gamification: From Theory to Exercise
I have been entailed with gamification for quite time currently. In my 9 years of experience, I have actually located video games are excellent at resolving several usual classroom problems such as: trainee participation/talk time, trainee involvement, differentiation, information tracking, and increasing trainee accomplishment.
As a secondary language educator on Jeju Island in South Korea, gamification aided me increase student talk time by 300 %. My 250 students finished over 27, 000 ‘missions,’ a.k.a. added research assignments they chose to do. My leading 10 % of participants invested an hour beyond course talking their target language daily. I was also surprised on greater than one occasion to arrive early to work and locate my trainees had actually defeated me there and were eagerly awaiting my arrival so they could begin their everyday missions.
As a classroom educator in the Houston Independent School area serving schools with a 95 % totally free and minimized lunch population, I have instructed both 3 rd- quality analysis and 5 th- grade scientific research. Each of these is a state-tested subject (that I instructed for two years).
Usually in my first year of instruction, my students have actually done 1 39 times the district norm and 1 82 times the district norm in my 2nd year teaching the topic. Or rephrase, standard techniques would take 14 to 18 months to attain what I can do with games in 10
I credit much of this success to adhering to the recommendations of Gabe Zicherman from his Google Tech Talk, Fun is the Future: Understanding Gamification , where he advises video game designers to “incentivize whatever you want people to do.” (Zicherman, n.d.)
Therefore I strive to identify the vital actions my students require to exercise then develop games and reward systems around those actions.
Gamification in education and learning makes use of the auto mechanics of games– factors, degrees, competitors, obstacles, and benefits– to inspire students and make learning more interesting. Below are 20 practical, classroom-tested instances of gamification that instructors can make use of to boost motivation and participation.
1 Offering Points for Meeting Academic Goals
Do students require to cite information from the message and support verdicts with evidence? Award 1 factor for a solution without proof, 2 factors for one item of evidence, and 3 factors for several pieces of proof. This makes evidence-based assuming quantifiable and inspiring.
2 Providing Factors for Procedural or Non-Academic Objectives
Wish to reduce the time it takes to check homework? Award 2 indicate every student that has their exercise prior to being prompted. This gamifies treatments and encourages self-management.
3 Creating Lively Barriers or Difficulties
Introduce enjoyable obstacles — puzzles, puzzles, or time-based challenges– that trainees need to overcome to open the next action of a lesson. These barriers increase interaction and mirror the challenge-reward loophole in games.
4 Developing Healthy And Balanced Competition in the Class
Attempt Educator vs. Class : Pupils earn factors collectively when they adhere to regulations; the instructor gains factors when they don’t. If trainees win, award them with a 1 -minute dance celebration, extra recess, or reduced research.
5 Contrasting and Reflecting on Efficiency
After a task, offer students with a performance break down — badges for creativity, synergy, or willpower, plus statistics like “most concerns asked” or “greatest variety of drafts.” Representation is a core element of gamification.
6 Producing a Series Of One-of-a-kind Incentives
Deal tiered incentives that appeal to various personalities. As an example: sunglasses for 5 factors, shoes-off advantage for 10, a positive moms and dad message for 15, or the right to “swipe” the instructor’s chair for the highest possible marker.
7 Making Use Of Levels, Checkpoints, and Development
Track points over several days or weeks and let trainees level up at milestones. Greater levels open opportunities, coach duties, or bonus obstacles– mirroring computer game progression systems.
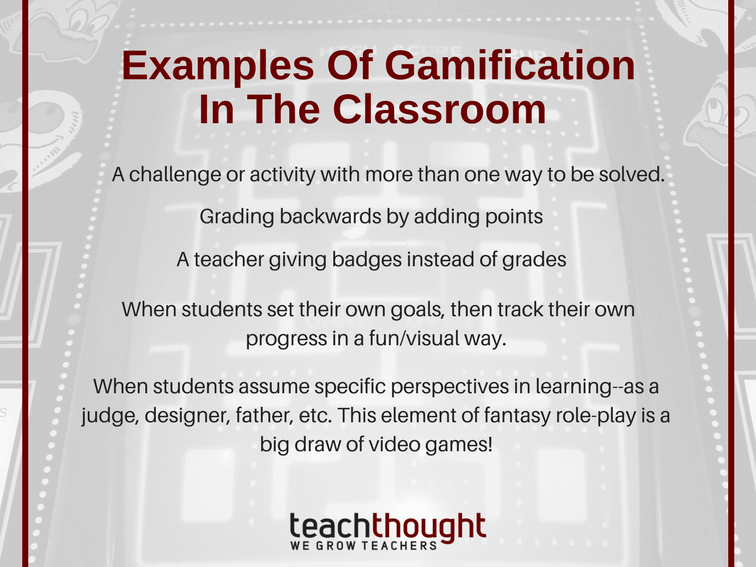
8 Rating Backward
Instead of beginning with 100, let pupils earn factors towards proficiency Each appropriate solution, ability demo, or positive behavior moves them closer to 100 This method reframes discovering as development as opposed to loss evasion.
9 Producing Multi-Solution Difficulties
Layout tasks with more than one legitimate service and motivate pupils to compare strategies. Compensate creative or special solutions to urge different thinking.
10 Utilizing Understanding Badges
Rather than (or alongside) grades, use digital or paper badges for achievements like “Crucial Thinker,” “Cooperation Pro,” or “Master of Portions.” Badges make discovering goals tangible and collectible.
11 Allowing Pupils Establish Their Own Goals
Permit pupils to establish tailored goals, then track their progress visually on a class leaderboard, sticker graph, or digital tracker. Self-directed goal-setting is motivating and shows ownership.
12 Assisting Students Think Roles or Personas
Use role-play to have trainees function as courts, designers, or historians while dealing with assignments. Role-based knowing take advantage of the immersive nature of video games.
13 Class Quests and Storylines
Cover devices or lessons in a narrative arc (e.g., “Survive the Ancient World”) where students open brand-new “chapters” by completing projects.
14 Time-Limited Boss Battles
End an unit with a joint evaluation challenge where trainees should “beat the one in charge” (respond to a set of tough problems) prior to the timer goes out.
15 Randomized Benefits
Use a secret incentive system : when students earn enough factors, allow them draw from an incentive container. The unpredictability maintains inspiration high.
16 Digital Leaderboards
Create a leaderboard for advancing factors, badges, or finished obstacles. Public recognition encourages competitive trainees however ought to be framed favorably to prevent shaming reduced entertainers.
17 Power-Ups for Positive Behavior
Introduce power-ups such as “added hint,” “avoid one research problem,” or “sit anywhere pass.” Students can spend gained indicate trigger them.
18 Cooperative Course Goals
Establish a shared unbiased — if the entire class satisfies a point total amount, they gain a group reward like a read-aloud day, a project event, or incentive recess.
19 Daily Streaks
Track everyday engagement or research completion with touch auto mechanics like those used by language-learning apps. Damaging a touch resets progress, urging consistency.
20 Unlockable Bonus Web Content
Give benefit activities or secret levels (puzzles, video clips, enrichment issues) that pupils can open after fulfilling a point limit. This gives advanced pupils extra obstacles.
Why Gamification Functions
Gamification transforms regular tasks right into engaging obstacles, urges innate and extrinsic inspiration, and offers continuous responses. When used thoughtfully, it advertises mastery, cooperation, and a feeling of development.
Discover more about gamification in finding out , check out game-based understanding methods , and obtain ideas for enhancing student interaction
Perk: Utilizing a scoreboard seating graph
Draw or forecast a seating graph onto a whiteboard/screen, and then honor trainees points for all activities that you wish to incentivize with sustainable rewards/recognitions at various factor degrees.
Final thought
See to it to be imaginative and react to student rate of interests. In my course, trainees don’t take technique tests; they battle the evil emperor, Kamico (the maker of preferred test preparation workbooks used at my institution). We don’t simply evaluate items for conductivity; we find the secret things which will certainly switch on the unusual spacecraf’s ‘prepared to release’ light.
While trainees are accumulating factors, leveling up, and competing against each other, I am accumulating information, tracking progression, and tailoring the policies, benefits, and pursuits to construct positive class culture while pressing pupil accomplishment. Trainees come to be eager to join the activities that they need to do to enhance, and when students buy-in, they make school a video game worth playing.
References & & More Checking out
McGonigal, J. (2011 Gaming can make a much better globe.|TED Talk|TED.com [Video file] Gotten from: ted.com/
Schaaf, R., & & Mohan, N. (2014 Making school a video game worth having fun: Digital games in the class SAGE Publications.
Schell, J. (n.d.) When games attack real life.|TED Talk|TED.com [Video file] Fetched from https://www.ted.com/talks/jesse_schell_when_games_invade_real_life
Zicherman. (n.d.). Enjoyable is the Future: Mastering Gamification [Video file] Retrieved from youtube.com
12 Examples Of Gamification In The Class